A Comprehensive Analysis
The Business Outlook Survey and the Business Leaders' Pulse indicate that firms have observed a restoration of confidence in their prospects with respect to sales expansion anticipations and overall business sentiment. However, sluggish demand persists, resulting in a relaxation of labor market conditions and a reduction in price pressures. As a result, a reduced number of companies are contemplating substantial or recurrent increases in prices in the coming year, in comparison to the findings of the previous survey. In this Greenlight Capital comprehensive analysis we’ll explore the first quarter business outlook of 2024.
Business Sentiment: A Weak Outlook with Encouraging Signs of Recovery
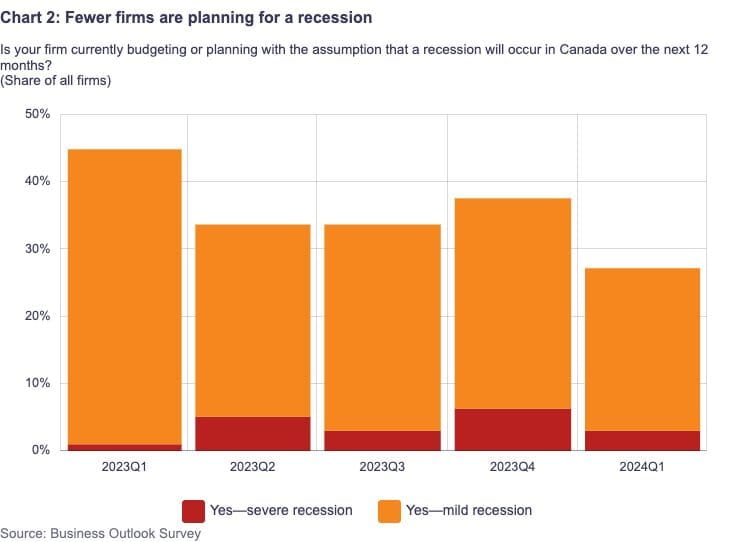
A modest recovery in business sentiment during the initial quarter follows an extended period of deterioration, suggesting the possibility of an overall improvement in business conditions. A positive trend is evident in numerous sectors, geographical areas, and organizational magnitudes. Additionally, compared to the previous quarter, fewer companies anticipate a recession in Canada within the next year.
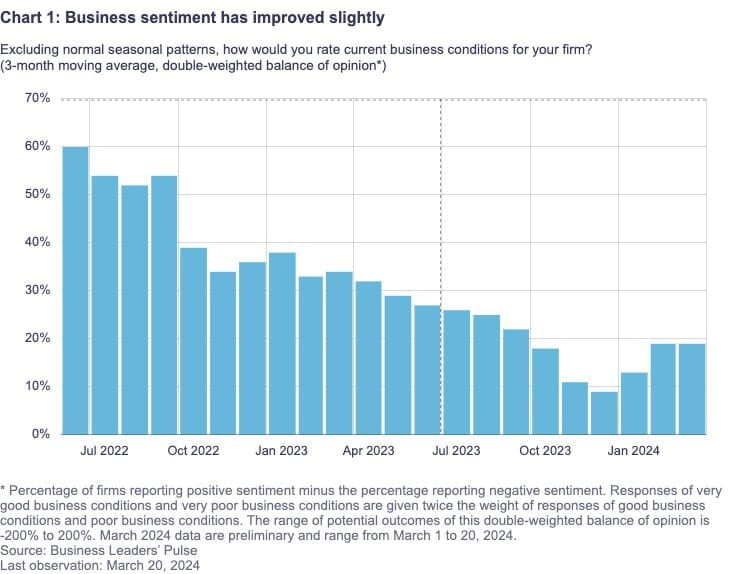
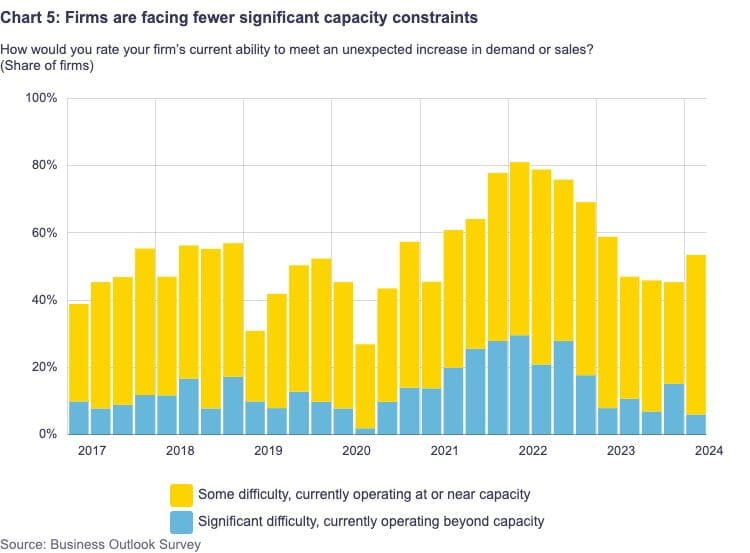
There are fewer problems that businesses face because of capacity constraints, such labor shortages and supply chain interruptions. These days, demand variations, unpredictability, and loan availability are their main worries. There is still a lot of pressure on costs; almost half of all businesses are seeing higher-than-normal expense rises. In addition, compared to prior quarters, a greater number of firms are voicing worries over taxes, industry-specific rules, and regional laws.
Impact of Interest Rates on Business Demand
Soft signs of demand and slow sales growth are two of the many variables that continue to impact the market for products and services. Many companies blame the current economic recession in Canada and the financial circumstances of their clients for the lackluster demand. A sizable portion of businesses claim that interest rates are hurting their operations, mostly via decreasing demand. This tendency is broad across industries and has remained steady over the last several quarters.
Businesses anticipate continued slow economic activity in the near future. Order books and advance reservations, two measures of potential future sales, have not much improved from the previous year. Businesses generally predict modest economic growth, and future sales growth will likely resemble that of the present age.
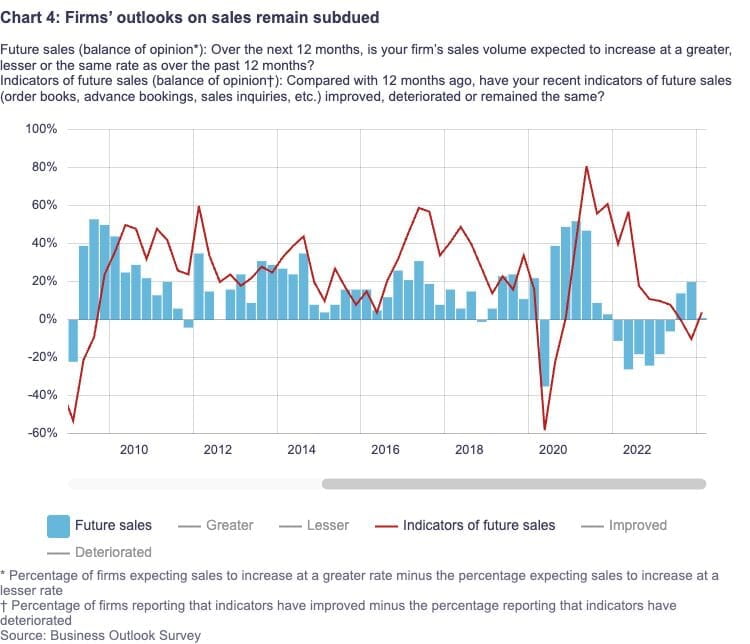
After many quarters of decline, evidence is starting to point in the direction of renewed confidence over demand. Businesses who have suffered from lower consumer spending in the last year specifically anticipate more sales growth in the next year. About half of the firms that said they expected sales growth to pick up speed in the next year also said they expected financing rates to drop. This conditional anticipation of a rebound in sales growth is especially noticeable in interest rate-sensitive industries like the housing market. Numerous businesses also said that strong population growth will continue to boost their revenues in the future. However, a lot of people are taking the initiative to increase their clientele, for example:
Stepping up marketing while maintaining competitive pricing.
Adjusting offers of goods and services to reflect customers' increased budgetary constraints.
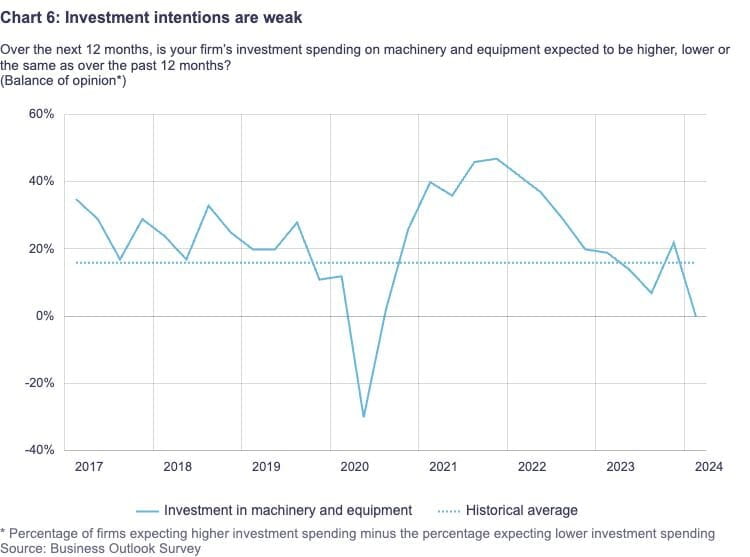
In this case, businesses' investment plans are weaker than they were in the past. This cautious investment stance is attributed to the following reasons:
Enduring unpredictability and muted market demand overall.
Less restrictions on output capacity.
Increased borrowing-related expenses.
Recent drops in the price of several commodities, most notably natural gas.
One possible explanation for the decline in investment intentions is the lingering impact of earlier interest rate increases. These days, a lot of long-term projects that were started while interest rates were lower are being finished. Many businesses are focusing their investment efforts on maintaining their present production capacities by repairing or upgrading their existing gear and equipment rather than taking on new projects to increase productivity or expand operations.
Declining Labour Shortages, Persistent Wage Growth
Labour Shortages
A recent survey reveals that less than a quarter of businesses are facing significant challenges in finding suitable workers, indicating a decrease in labor market tightness compared to a year ago. This shift is attributed to a combination of reduced demand for new employees and an increased availability of workers.
Hiring Intentions
Despite the overall easing of labor conditions, 43% of firms are planning to expand their workforce in the next year. This intention is fueled by improving business sentiment, slightly better demand projections, and a more balanced labor market scenario.
Companies expect salary growth to be slower in the next year than it was in the previous one because of a more flexible labor market. They nonetheless want to raise pay by an average of 4.1%, which is more than typical, in spite of this. When determining pay, a significant portion of enterprises take the high cost of living into account. Although the cost of living affects over 60% of businesses, less than one-third believe that pressure on pay increases is intensifying in comparison to the previous year. Companies expecting more than 3% inflation in the next year plan to raise wages more significantly. With slightly over 40% of employers stating that their salary increases are no longer particularly large, the return to regular wage setting is happening gradually. Nonetheless, from 14% in the prior quarter to 23% now, companies anticipate exceptionally strong wage growth to continue until 2025.
Declining Inflation Expectations in Business Outlook
The latest data shows a steady decline in short-term inflation expectations. This trend is attributed to the belief among firms that monetary policy is effectively easing inflationary pressures arising from both demand and capacity constraints. However, the slowdown in inflation expectations is being tempered by rising costs associated with housing, food, and wages.
Decrease in Long-Term Inflation Expectations
According to the Business Outlook Survey, only 27% of firms anticipate inflation to remain above 2% for more than three years. This percentage has decreased from 37% in the previous quarter, indicating a diminishing expectation of sustained higher inflation rates in the long term.
Final Thoughts
Business sentiment shows signs of improvement, the overall outlook remains cautious as demand continues to lag. Greenlight Capital's analysis reveals a nuanced landscape where sales growth expectations have stabilized, yet concerns persist regarding subdued demand, cost pressures, and investment intentions. Despite easing labor shortages, wage growth remains relatively high, impacting pricing behavior. However, there's optimism surrounding a potential turnaround fueled by expectations of declining interest rates and population growth. The moderation in inflation expectations suggests a balancing act between monetary policy and cost dynamics. Amidst these complexities, businesses are adapting strategies to navigate uncertainties, including adjusting pricing strategies, investing cautiously, and managing wage pressures. Contact Greenlight Capital for more information.



